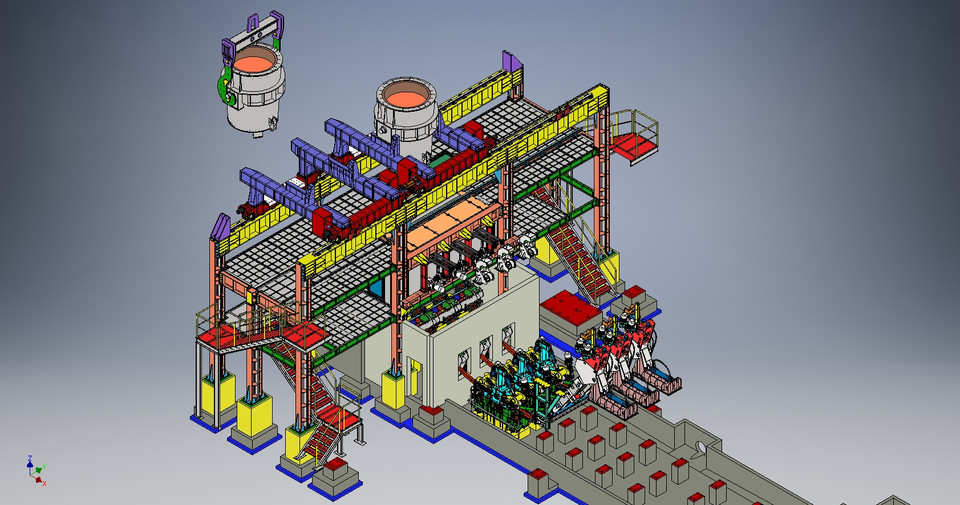
Continuous Casting Machines: Revolutionizing Steel Production
The advent of continuous casting machines (CCMs) marks a significant milestone in the steel industry. In the ever-evolving landscape of steel production, these machines have revolutionized the way molten steel is transformed into various forms, enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and minimizing environmental impact. This article delves deep into the world of continuous casting, exploring its mechanisms, advantages, and the transformative impact it has had on the steel manufacturing sector.
Outline of the Article:
- The Genesis of Continuous Casting
- Historical Evolution
- Early Challenges and Innovations
- How Continuous Casting Works
- The Fundamental Process
- Types of Continuous Casting Machines
- Advantages of Continuous Casting
- Enhanced Product Quality
- Increased Production Efficiency
- Cost-effectiveness and Waste Reduction
- Continuous Casting in Various Steel Forms
- Billets and Blooms
- Slabs
- Rods and Wires
- Technological Innovations in Continuous Casting
- Automation and Robotics
- Advanced Cooling Systems
- Environmental Sustainability
- Reduced Emissions
- Energy Efficiency
- Challenges and Solutions
- Quality Control Measures
- Addressing Material Variability
- Continuous Casting Around the Globe
- Notable Installations
- Impact on Global Steel Market
- Future Trends and Developments
- Smart Casting Technologies
- Integration with Industry 4.0
- Conclusion
- Recap of Key Benefits
- The Future of Continuous Casting
Introduction:
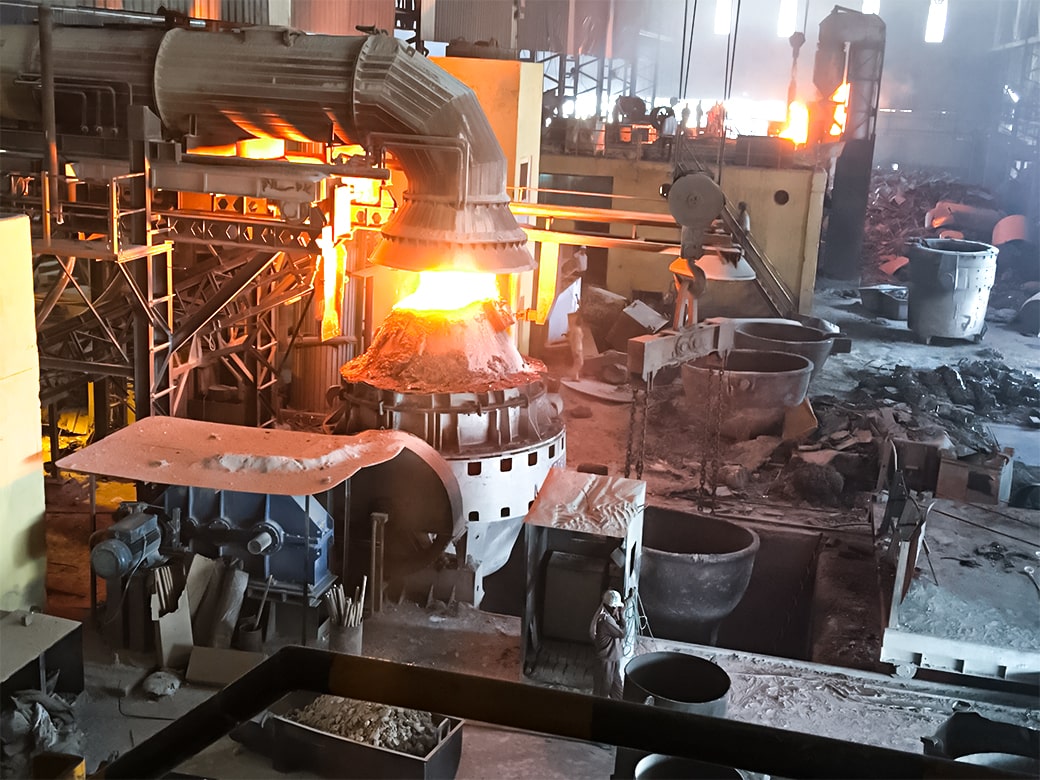
Continuous casting, an innovative method in steel production, has reshaped the industry’s landscape. Unlike traditional methods, where molten steel is poured into molds and then solidified, continuous casting involves a non-stop process where steel is cast into various forms directly from its liquid state. This seamless process not only boosts production efficiency but also significantly improves the quality of the final product.
How Continuous Casting Works:
Continuous casting operates on a simple yet ingenious principle. Molten steel is poured into a tundish, a refractory-lined reservoir, from which it flows into a water-cooled copper mold. As the steel cools and solidifies against the mold walls, it begins its transformation into various shapes. The continuous movement of the mold ensures a constant feed of solidifying steel, resulting in a continuous strand of the desired form.
Advantages of Continuous Casting:
Continuous casting brings several advantages to the table. Firstly, it enhances product quality by reducing the occurrence of defects like inclusions and segregations. Moreover, the continuous process ensures a more consistent grain structure, enhancing the steel’s mechanical properties. Secondly, this method significantly boosts production efficiency. Traditional casting methods face downtime during mold changes, a drawback eliminated by continuous casting. Additionally, the process allows for the production of a wide array of steel shapes and sizes, including billets, slabs, rods, and wires.
Continuous Casting in Various Steel Forms:
Continuous casting technology caters to diverse steel products. For instance, it produces billets and blooms, essential raw materials for various downstream applications. Slabs, the starting point for flat steel products like sheets and coils, are also efficiently manufactured through this method. Furthermore, continuous casting is ideal for producing long products such as rods and wires used in construction and industrial applications.
Technological Innovations in Continuous Casting:
Continuous casting has evolved with technological advancements. Automation and robotics have streamlined the process, ensuring minimal human intervention and higher precision. Advanced cooling systems, employing a combination of water and air cooling, have been pivotal in maintaining the ideal temperature gradients for solidification.
Environmental Sustainability:
Apart from its efficiency and quality benefits, continuous casting contributes significantly to environmental sustainability. By reducing the need for reheating and minimizing material wastage, this method lowers energy consumption and emissions. The efficient use of resources aligns with the steel industry’s global efforts toward eco-friendly practices.
Challenges and Solutions:
Despite its numerous advantages, continuous casting faces challenges related to quality control and material variability. However, advancements in sensing technologies, data analytics, and machine learning have paved the way for real-time monitoring and process optimization. These innovations ensure a higher degree of control over the final product’s quality and consistency.
Continuous Casting Around the Globe:
Continuous casting installations are prevalent worldwide. Notable steel producers across continents have adopted this technology, driving its global market growth. The impact of continuous casting is not confined to individual companies; it shapes the entire steel industry’s dynamics.
Future Trends and Developments:
The future of continuous casting lies in smart technologies and Industry 4.0 integration. Smart casting technologies leverage real-time data to optimize the casting process further. These advancements, coupled with the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence, promise enhanced efficiency, predictive maintenance, and overall process improvement.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, continuous casting machines have redefined steel production standards. Their ability to ensure superior product quality, enhance production efficiency, and contribute to environmental sustainability underscores their pivotal role in the modern steel industry. As the technology continues to evolve, it will remain at the forefront of innovations, driving the industry toward a more efficient, sustainable, and high-quality future.
FAQs:
- What are the primary advantages of continuous casting over traditional methods?
- How has continuous casting impacted the steel industry’s environmental footprint?
- What challenges does continuous casting face in terms of quality control, and how are these challenges addressed?
- Which countries are leading in the adoption of continuous casting technologies?
- What role does automation play in optimizing the continuous casting process?